Present Progressive/Kontrastierung: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(l) Markierung: Quelltext-Bearbeitung 2017 |
Markierung: Quelltext-Bearbeitung 2017 |
||
| (Eine dazwischenliegende Version desselben Benutzers wird nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
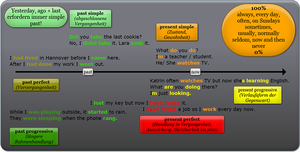
Die konsequente Verwendung der Zeiten wird dadurch erschwert, dass es die Verlaufsform ([[Present Progressive|Present Progressive]]) im Deutschen so nicht gibt. | Die konsequente Verwendung der Zeiten wird dadurch erschwert, dass es die Verlaufsform ([[Present Progressive|Present Progressive]]) im Deutschen so nicht gibt. | ||
Deshalb muss klar analysiert werden, ob Handlungen und Tätigkeiten regelmäßig stattfinden (oft durch [[ | Deshalb muss klar analysiert werden, ob Handlungen und Tätigkeiten regelmäßig stattfinden (oft durch [[Adverbs/Adverbs of Frequency|''adverbs of Frequency'']] angezeigt) oder ob betont werden soll, dass etwas gerade oder nur vorübergehend geschieht (Signalwörter: Look! Listen! just, now …). | ||
[[Datei:Present Progressive-4.svg|Infografik: Kontrastierung Present Simple vs. Present Progressive]] | [[Datei:Present Progressive-4.svg|Infografik: Kontrastierung Present Simple vs. Present Progressive]] | ||
| Zeile 74: | Zeile 74: | ||
In the background a man ''is now diving (<span style="background:yellow">now</span>, dive)'' into the sea. Ben who ''is lying (lie)'' on his surfboard ''shouts (shout)'': "What ''are you doing(you, do)''? I'm falling into the water!" | In the background a man ''is now diving (<span style="background:yellow">now</span>, dive)'' into the sea. Ben who ''is lying (lie)'' on his surfboard ''shouts (shout)'': "What ''are you doing(you, do)''? I'm falling into the water!" | ||
Three teenagers ''are playing (play)'' beach volleyball. They '' | Three teenagers ''are playing (play)'' beach volleyball. They ''practice (practice)'' <span style="background:orange">two times a week</span>. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Zeile 83: | Zeile 83: | ||
In the background a man ''is now diving (<span style="background:yellow">now</span>, dive)'' into the sea. Ben who ''is lying (lie)'' on his surfboard ''shouts (shout)'': "What ''are you doing(you, do)''? I'm falling into the water!" | In the background a man ''is now diving (<span style="background:yellow">now</span>, dive)'' into the sea. Ben who ''is lying (lie)'' on his surfboard ''shouts (shout)'': "What ''are you doing(you, do)''? I'm falling into the water!" | ||
Three teenagers ''are playing (play)'' beach volleyball. They '' | Three teenagers ''are playing (play)'' beach volleyball. They ''practice (practice)'' <span style="background:orange">two times a week</span>.}} | ||
=== some questions === | === some questions === | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 15. Januar 2024, 07:18 Uhr
Die konsequente Verwendung der Zeiten wird dadurch erschwert, dass es die Verlaufsform (Present Progressive) im Deutschen so nicht gibt.
Deshalb muss klar analysiert werden, ob Handlungen und Tätigkeiten regelmäßig stattfinden (oft durch adverbs of Frequency angezeigt) oder ob betont werden soll, dass etwas gerade oder nur vorübergehend geschieht (Signalwörter: Look! Listen! just, now …).
Remember? Use the Present Progressive for actions which happen now and the Present Simple for regular actions.
Interaktive Übungen
- Watch the video and do the tasks.
- Then do the other exercises below.
A day with David
Every day David gets up at 7 o'clock.
It is 7 o'clock. David is getting up now.
David always goes to school at 8 o'clock. It is 8 o'clock now. David is going to school.
Before he goes to school, he always puts on his school uniform. He is putting it on now.
It is 3 o'clock now. He is coming home from school.
He usually comes home at 3.15.
In the afternoon
Write in the correct forms - present simple or present progressive.
Every afternoon he does (do) his homework. It is 4 o'clock. He is doing (do) it now.
In the afternoon the children often play (play) football. He is playing (play) it just now.
Then the Millers usually have (have) dinner. Today they are having (have) Chinese food.
It is 7 o'clock now and David is watching (watch) TV. He watches (watch) TV every evening.
Every evening David cleans (clean) his teeth. After that he always goes (go) to bed.
In the afternoon the children often play (play) football. He is playing (play) it just now.
Then the Millers usually have (have) dinner. Today they are having (have) Chinese food.
It is 7 o'clock now and David is watching (watch) TV. He watches (watch) TV every evening.
Every evening David cleans (clean) his teeth. After that he always goes (go) to bed.
On the beach
Look, the family is playing (play) with the ball. They come (come) to the beach very often.
Listen! Becky is listening (listen) to the radio. Her favourite radio station always plays (play) good music. Simon usually reads (read) a book on the beach. He is doing (do) that at the moment.
In the background a man is now diving (now, dive) into the sea. Ben who is lying (lie) on his surfboard shouts (shout): "What are you doing(you, do)? I'm falling into the water!"
Three teenagers are playing (play) beach volleyball. They practice (practice) two times a week.
Listen! Becky is listening (listen) to the radio. Her favourite radio station always plays (play) good music. Simon usually reads (read) a book on the beach. He is doing (do) that at the moment.
In the background a man is now diving (now, dive) into the sea. Ben who is lying (lie) on his surfboard shouts (shout): "What are you doing(you, do)? I'm falling into the water!"
Three teenagers are playing (play) beach volleyball. They practice (practice) two times a week.
some questions
Make questions and then give short answers.
1. Does the teacher ask Samira about her homework? - Yes, she does.
2. Is Mrs Foster at home? - No, she isn't.
3. Do the children often talk in the lesson? - No, they don't.
4. Is Timon now doing his homework? - Yes, he is.
5. Does Feline always do her homework? - No, she doesn't.
Present Progressive
(Verlaufsform der Gegenwart)
- Exercises
- Verneinung und Fragen
- Kontrastierung (Gegenüberstellung) von Present Progressive und Simple Present
Past Tense:
Present Tense: