Diese Grundwissenseite dient als Übersicht über die wichtigsten Begriffe im Zusammenhang mit Termen.
Begriffe
Term: Ein Term ist ein Rechenausdruck, der einen Sachverhalt beschreibt und neben Zahlen auch Variablen enthalten kann.
Variable: Eine Variable ist ein Platzhalter (häufig Buchstaben), der durch verschiedene Einsetzungen ausgetauscht werden kann.
Definitionsmenge : Die Definitionsmenge ist die Menge der Zahlen, die bei der Einsetzung für eine Variable in einen Term zu einer sinnvollen Aussage führen.
Termwert: Der Termwert ist das Ergebnis, das man erhält, wenn man in den Term eine Zahl der Definitionsmenge einsetzt.
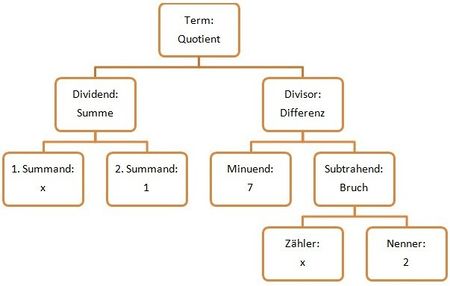
Termart: Die Termart wird durch das letzte ausgeführte Rechenzeichen festgelegt. (mehr Information)
Rechengesetze
Kommutativgesetz


- für alle a, b, c

Assoziativgesetz


- für alle a, b, c

Distributivgesetz


- für alle a, b, c,


 =
=  +
+  bzw.
bzw.

 =
=  -
-  bzw.
bzw.

- für alle a, b, c,

Klammerregeln